Software-Defined Networking (SDN) & SD-WAN Explained
In today’s fast-moving digital world, businesses need networks that are flexible, secure, and cloud-ready. This is where Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN) come into play. Both technologies are reshaping how enterprises design, manage, and secure their networks.
What is Software-Defined Networking (SDN)?
SDN (Software-Defined Networking) is a modern networking approach where the control plane is separated from the data plane. Instead of relying only on physical devices (routers and switches), SDN introduces a centralized controller that manages the entire network.
Key Features of SDN:
-
Centralized Control: One dashboard to manage all network devices.
-
Programmability: Easy to configure networks using APIs.
-
Automation: Reduced manual configuration tasks.
-
Flexibility: Adapts quickly to new business applications.
👉 Example: Telecom providers and ISPs use SDN to automate FTTH (Fiber-to-the-Home) provisioning, making services faster and more reliable.
What is Software-Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN)?
SD-WAN is a subset of SDN that specifically focuses on WAN (Wide Area Networks), connecting branch offices, data centers, and cloud platforms.
Instead of using only expensive MPLS lines, SD-WAN combines broadband, LTE, and fiber connections intelligently, providing cost savings and better performance.
Key Features of SD-WAN:
-
Dynamic Path Selection: Chooses the best link (MPLS, fiber, LTE, or broadband) for traffic.
-
Cloud Optimization: Direct connections to cloud services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
-
Enhanced Security: Built-in firewalls, encryption, and Zero Trust models.
-
Cost Savings: Uses affordable internet links instead of costly MPLS.
👉 If you’re interested in career growth, check out Best Cisco Certifications to Pursue in 2025.
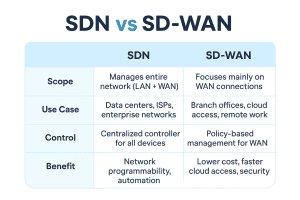
Difference Between SDN and SD-WAN
| Feature | SDN | SD-WAN |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Manages entire network (LAN + WAN) | Focuses mainly on WAN connections |
| Use Case | Data centers, ISPs, enterprise networks | Branch offices, cloud access, remote work |
| Control | Centralized controller for all devices | Policy-based management for WAN links |
| Benefit | Network programmability, automation | Lower cost, faster cloud access, security |
Cisco’s Role in SDN & SD-WAN
Cisco is one of the pioneers in both SDN and SD-WAN solutions.
-
Cisco ACI (Application Centric Infrastructure): Cisco’s SDN platform that automates and secures data center networks.
-
Cisco SD-WAN (Viptela & Meraki): Provides intelligent WAN routing, cloud integration, and advanced security.
-
AI Integration: Cisco uses AI-driven insights to optimize both SDN and SD-WAN performance.
👉 For a deeper look, visit Cisco SD-WAN official documentation (external link).
Why Businesses are Adopting SDN & SD-WAN
-
Cloud-First Strategy: Easier access to SaaS and IaaS platforms.
-
Remote Workforce: Secure and optimized connections for WFH employees.
-
Network Agility: Quick deployment of new applications and services.
-
Cost Efficiency: Reduced reliance on traditional MPLS.
Conclusion
Both SDN and SD-WAN are critical for building future-ready networks. While SDN focuses on automation and programmability, SD-WAN ensures cost-effective and secure WAN connectivity. With Cisco, enterprises can confidently adopt these technologies to support cloud, remote work, and AI-driven business needs.